|
Di seguito gli interventi pubblicati in questa sezione, in ordine cronologico.
This recipe made last night a Saturday night to remember.
Turned out beautiful and talk about delicious, this recipe is highly recommended.
Marihuana Pizza
Delicious homemade pizza with a cannabis ghee based crust and topping.
Estimated Time: about 1 hour
Serves: Makes 2 Pizzas

Ingredients:
Dough:
3 1/2 cups all-purpose flour
1oz/28g yeast
1 tbsp granulated sugar
1 cup/8 fl oz warm water
1 tsp salt
2 tbsp melted cannabis ghee
Toppings:
4-5 tbsp melted cannabis ghee
2 cups grated cheese
1-2 cans chopped tomatoes
1 1/2tsp fresh oregano (or other spices and herbs)
other optional toppings: mushrooms, pepperoni, peppers, etc.
Instructions:
To make the dough add the flour, yeast, and sugar into a large bowl. Add water, and knead into dough. Cover with a cloth and leave in warm place to rise for 30 minutes. Add the salt and melted ghee to the dough and knead into a ball. Coat with flour. Saute the vegetable toppings in the cannabis ghee. (Don't over-do it!) Add tomatoes and oregano and allow to simmer until it has a sauce-like consistency. Roll dough into two circles. Add sauce, toppings and cheese. Bake for 10-15 minutes at 400°F
Enjoy
Click the link below for more great stuff...
Source: CookingWithCannabis
Makes six servings.
4 cups tart apples, pared, cored and sliced
2 tablespoons lemon juice
1/2 cup all-purpose flour
1/2 cup brown sugar
1/4 cup Canna Butter*
1/2 teaspoon salt
1 teaspoon cinnamon

Preheat oven to 375 degrees. Put the apples into a 9-inch pie pan or dish and add the lemon juice. In a large mixing bowl add the remaining ingredients and work the mixture with a pastry blender or your fingers. Lightly blend them so they do not become oily. Spread the crumbly mixture over the apples. Bake for about 30 minutes.
Serve hot. Click the link below for more cool stuff...
Source: CookingWithCannabis
This is delicious, you must try it.
Ingredients:

Baking spray
2 sticks canna-butter, room temperature, or use less medicated butter and more without cannabis
2 & ˝ cups sugar, divided into 2 cups and ˝ cup
2 large eggs, lightly beaten
2 cups (1 pint) sour cream
1 tablespoon vanilla
2 cups all purpose flour
1 tablespoon baking powder
Ľ teaspoon salt
1 cup walnuts, chopped
1 cup chocolate chips
1 tablespoon cinnamon
˝ teaspoon ground cardamom
Directions:
One of the great edible pleasures in life is a moist piece of buttery cinnamon coffee cake with just the right amount of streusel and swirl; two easy baking steps to master. This cake has been present for every one of our News Year's Day breakfasts for over 14 years. It didn't always have a boatload of weed in it, as it does in this recipe, but when I thought of foods that would be perfect when medicated this came quickly to mind. It's
pretty easy to make. Lots of butter, so a perfect recipe for a medicated make-over. When cooking with marijuana, you need fat (butter, all cooking oils, milk products that are not non-fat) because the THC will cling to the fat when heated. So, for example, if you make hot cocoa, and you use non-fat milk, the potency will be radically different than if you used 2% or whole milk.
Back to the cake. There is something very comforting about a coffee cake. This one has a good amount of vanilla, chocolate chips and walnuts, and a tasty streusel topping that has a touch of cardamom and healthy dose of cinnamon. It is super with a cup of coffee or tea, and is not half bad with a scoop of ice cream nested on the top. One of the local shops in my town does a cardamom ice cream that when placed on the top of a slice of this the cake causes great sighs, swoons and smiles due to the high level of deliciousness!
Heat oven to 325.
Spray a 9 x 13 inch baking pan.In a small bowl, mix 1/2 cup of the sugar with the walnuts, chocolate chips, cinnamon and cardamom. Set aside. In a large mixing bowl cream together the butter and 2 cups of sugar. Add eggs, blending well, then the sour cream and vanilla.Sift the flour, baking powder, and salt. Fold the dry ingredients into the creamed mixture, and beat until just blended.
Do not overbeat. Pour one-third of the batter into the prepared pan.
Sprinkle with half of the nut/chocolate mixture. Repeat. Then add remaining batter.Bake until the center of the cake is set, about 50-60 minutes. A cake tester or toothpick inserted in the center should come out clean. Oven temps can vary quite a bit, so please check for doneness after 45 minutes, it's a bummer if this delicious cake is overcooked.
Check out the link below for some awesome information...
Source: CookingWithCannabis
Neuropathic and inflammatory pain
Nociception (pain perception) is a critical mechanism of the body self-defence, inducing to discontinue a stimuli potentially deteriorating.
When pain is experienced chronically,often as a consequence of a neural or metabolic dysfunction, as in the case of neuropathic pain (NP), it is fundamental to find agents able to target the pathways producing allodynia (sensation of pain evoked by a stimulus which would not, normally, produce it) and ultimately to eradicate them. [1]
It has been estimated that 7-8% of the entire population of Western Countries develops neuropathic pain, which is often caused by other pathologies (cancer, diabetes, Multiple Sclerosis, HIV or stroke, just to mention a few).[2]
Despite the aetiology of the disease is multifarious, it causes the nervous system to be hypersensitised due to prolonged impulses.
Neuropathic pain alone is a chronic debilitating disease that affects up to 4 million people just in Europe; given the poor outcome of the medicines currently in use for the management of symptoms, (gabapentin, opioids and tricyclic antidepressant mainly) many studies are focussed on this field of study. [3]
Why using cannabinoids?
Phytocannabinoids have been extensively used throughout history for various therapeutic purposes, particularly analgesic. However, the cannabinoid circuitry is relatively young, with only 20 years since its first characterization by the pioneering studies of Raphael Mechoulam, whose discoveries conveyed these chemicals from traditional home remedies to pharmacological investigation. [4]
Since the discovery of Cannabinoid receptors pain regulation became one of the main area of study. Compelling evidence has shown that cannabinoids decrease allodynia both thermal and mechanical, proving their role for treating neuropathic pain. [5]
Cannabinoids vs opioids
The main mediator of the antinociceptive effect is thought to
be the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. The benefit of targeting directly CB1 receptors is endorsed by their anatomical distribution in core pain centers of the brain (Periaqueductal grey-substantia gelatinosa-medulla oblongata-dorsal horn). [6]
CB1 agonists (all the drugs that activate CB1 receptors, such as THC) prevent “wind-up” phenomenon in the dorsal horn (an exaggerated sensitization to pain leading to allodynia and hyperalgesia and hallmark of neuropathic pain). (Hyperalgesia =increased sensation to pain, usually due to damaged pain receptors and nerve terminals)
It is hence crucial to pinpoint that manipulating cannabinoid circuitry is more advantageous than targeting directly opioids for the treatment of neuropathic pain. [6, 7]
Moreover, the medicines that activate CB1 receptors maintain their efficacy, at the opposite of morphine, which is less potent over time (so that more doses are needed, and with it, an increase in side effects).
Importantly, the spontaneous discharge (which lead to pain sensation) has been located mainly in primary afferent myelinated A-fibres, which are rich in cannabinoid receptors rather than opioids. [8]
The current medications for treating pain are still mainly opioids, but only approximately 50% of the sufferers finds relief with the available cures, thus highlighting how the clinic would greatly benefit from drugs oriented on cannabinoids modulation. [2]
On the ring today...
Opioids are prescribed worldwide to deal with pain.
Only recently Sativex has been approved for treatment of pain in 2 Countries only! If you want to know more click here.
Here are some facts, all the side effects, both very common and rare for both medications.
Remember that researching cannabinoids medications does not necessarly mean using THC-based medications and lots of research is going through in this direction, making cannabinoid-based drugs even safer and non-psychoactive.
| Side effects |
Cannabis |
Morphine |
| |
|
blood pressure chages |
| |
|
constriction of the pupil of the eye |
| |
|
irregular heart rate |
| |
increased heart rate |
erectile dysfunction |
| Cardiovascular |
redness of the eyes |
eye or eyesight problems |
| |
vasodilatation/facial flush |
facialflushing |
| |
|
irregular heart rate |
| |
|
oedema of the extremities |
| |
|
palpitations |
| |
|
|
| |
aids sleeping |
difficult sleeping |
| Circadian |
somnolence |
sleepiness |
| |
|
|
| |
aids gastrointestinal functions (diarrhea is rare) |
biliary problems |
| Gastrointestinal |
anti-emetic, can cause nausea when overdosed |
constipation |
| |
eases cramps |
gastrointestinal problems |
| |
abdominal pain can occur (rare) |
indigestion |
| |
|
nausea |
| |
|
vomiting |
| |
|
stomachpain |
| |
|
|
| |
|
amenorrhoea |
| Hormonal |
|
decreased libido |
| |
|
|
| |
|
allergic reactions |
| |
|
anaphylactic reactions |
| Immunologic |
anti-inflamatory |
itching |
| |
|
skin rash or rashes |
| |
|
worsening of pancreatitis |
| |
|
urticaria |
| |
|
|
| Muscolar |
muscle relaxant |
abnormal muscle movement |
| |
unsteadiness |
muscle twitching |
| |
|
|
| |
|
confusion |
| |
|
drowsiness |
| |
|
headaches |
| |
|
loss of appetite |
| |
|
thinking problems |
| |
|
weakness |
| |
confusion |
convulsions |
| |
drowsiness |
dysphoria- euphoria |
| |
increased appetite |
fainting |
| |
weakness |
feeling agitated |
| Neurologic |
euphoria |
general feeling of being unwell |
| |
sense of well-being |
hallucinations |
| |
depersonalization |
mood changes |
| |
hallucination |
physical dependence |
| |
paranoid reaction |
psychological dependence |
| |
|
vertigo |
| |
|
withdrawal symptoms |
| |
|
|
| |
|
bronchospasm |
| Respiratory |
bronchodilator |
pulmonary oedema |
| |
|
respiratory depression |
| |
|
|
| |
|
severe dry mouth |
| |
|
sweating |
| Salivation |
dry mouth |
renal spasms |
| |
|
urinary retention |
List of references:
1. Scadding, J. (2003). Neuropathic Pain.ACNR. 3 (2), 8-14.
2. Mao, J., Price, D.D., Lu, J., Keniston, L., Mayer, D.J. (2000) Two distinctive antinociceptive systems in rats with pathological pain. Neurosci. Lett., 280, 13-16.
3. Selph, S Carson, S Fu, R et al. (2011). Drug Class Review Neuropathic Pain. Available: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov . Last accessed 4/3/13 .
4. British Medical Association (1997) Therapeutic Uses of Cannabis. London, Harwood Academic Publishers
5. Fox, A., Kesingland, A., Gentrym C., McNair, K., Patel, S., Urban, L., James, I. (2001) The role of central and peripheral Cannabinoid 1 receptors in the antihyperalgesic activity of cannabinoids in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain, 92, 91-100.
6. Martin, B.R., Lichtman, A.H. (1998) Cannabinoid transmission and pain perception. Neurobiol.Dis., 5, 447-461.
7. Lichtman, A.H., Martin, B.R. (1991) Spinal and supraspinal components of cannabinoid-induced antinociception. J.Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 258, 517-523.
Author: Viola Brugnatelli, BSc Neuroscience - Source: Casey McClain at naturegoingsmart.com/
Drinking Raw Cannabis Juice Cures BRAIN TUMORS - LEAF Documentary.
We just finished the english caption of the entire documentary. Please, help translate it in all the languages of the world so the people would know the truth about the magic of cannabis: dotsub . Join us on: DotSub subtitling group - facebook and on our website: http://www.TurismoAssociati.it/dBlog
It is no secret that our world is seeing a huge increase in poor health and cancer cases. It should come as no surprise when we look at what we eat daily, the condition of our environment and the types of body care products we use daily that contain a ton of cancer causing agents. Mainstream medicine suggests that chemotherapy and radiation are the best means to go about treating cancer, but there is a growing body of evidence to suggest there exist much better cures.
Cannabinoids may very well be one of the best disease and cancer fighting treatments out there. If you have heard of Rick Simpson you have heard of his methods of preparing cannabis or hemp in such a way where he is able to extract the oil from it and use that oil to treat cancer. Rick has been very successful in his work and his popularity is growing as a result. At the same time, he has received a great deal of flack for his methods as they pose a serious threat to the business that is cancer.
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids refer to any of a group of related compounds that include cannabinol and the active constituents of cannabis. They activate canbinoid receptors in the body. The body itself produces compounds called endocannabinoids and they play a role in many processes within the body that help to create a healthy environment. Cannabinoids also play a role in immune system generation and re-generation. The body regenerates best when it’s saturated with Phyto-Cannabinoids. Cannabinoids can also be found in Cannabis. It is important to note that the cannabinoids are plentiful in both hemp and cannabis. The differentiation between hemp and cannabis is simply that hemp only contains 0.3% THC while cannabis is 0.4% THC or higher. (Technically they are both strains of Cannabis Sativa.)
Cannabinoids have been proven to reduce cancer cells as they have a great impact on the rebuilding of the immune system. While not every strain of cannabis has the same effect, more and more patients are seeing success in cancer reduction in a short period of time by using cannabis. Contrary to popular thought and belief, smoking the cannabis does not assist a great deal in treating disease within the body as therapeutic levels cannot be reached through smoking. Creating oil from the plant or eating the plant is the best way to go about getting the necessary ingredients which are the cannabinoids. Another aspect of smoking the cannabis that must be looked at is the fact that when the cannabis is heated and burnt it changes the chemical structure and acidity of the THC which changes its ability to be therapeutic. Further, anytime you burn something and inhale it, you create oxidation within the body. That oxidation is not healthy for the body and can lead to health issues itself.
Cannabinoids can prevent cancer, reduce heart attacks by 66% and insulin dependent diabetes by 58%. Cannabis clinician Dr. William Courtney recommends drinking 4 – 8 ounces of raw flower and leaf juice from any Hemp plant.
Cannabis – whether Sativa, Indica, Ruderalis, male, female, hermaphrodite, wild, bred for fiber, seeds or medicinal resin – is a vegetable with every dietary essential we can’t synthesize: Essential Amino Acids, Essential Fatty Acids, Essential Cannabinoid acids and hundreds of anti-Cancer compounds. It is important to note that when we isolate to important compounds of cannabis and take them in supplement we miss out of the bio-synergistic compounds that go along with it in full plant form. This makes it more difficult for the body to determine what exactly it is taking in.
“If you heat the plant, you will decarboxylate THC-acid and you will get high, you”ll get your 10 mg. If you don’t heat it, you can go up to five or six hundred milligrams & use it as a Dietary Cannabis. . . and push it up to the Anti-oxidant and Neuro-protective levels which come into play at hundreds of milligrams,” stated Dr. William Courtney.
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) maintains our biological systems by regulating each cell tissue. It uses Arachadonic acid/Omega 6 to make Endo-Cannabinoids: fatty molecules that communicate harm between cells. Dietary Cannabis mimics the ECS by providing Cannabinoids when there is an Arachadonic acid deficiency or Clinical Cannabinoid Deficiency.
Doctors who have been researching cannabis and it’s benefits in diet for some time have recommended that people make cannabis a part of their everyday diet. To reiterate, the plant does not need to contain high levels of THC and it can simply be hemp. Eating Cannabis that does contain THC will not get you high. Also, smoking it does not give the same results as eating or juicing the plant. If we view the plant simple as a vegetable like all other vegetables we eat, it makes sense that we wouldn’t put it inside rolling papers and smoke it to get the nutritional benefits.
Sources: collective-evolution
rawhemp
phoenixtears
cannabisinternational
edrv.endojournals.org
cannabisclinicians
You would think that with the latest Operating System from Microsoft, Windows 8, it would be easy to connect a smartphone with Windows Phone OS. Think again.
It looks like Windows complicated the things, making it very difficult to manage a device. If you open the Manage Bluetooh devices (opening Search with Windows Key and Q and looking for Bluetooth), after you turn on Bluetooth you'll get: Your PC is searching for and can be discovered by Bluetooth devices... that will never stop searching. And furthermore, sometimes, just sometimes, you'll get the Pair Devices option to recognise the phone and pc.
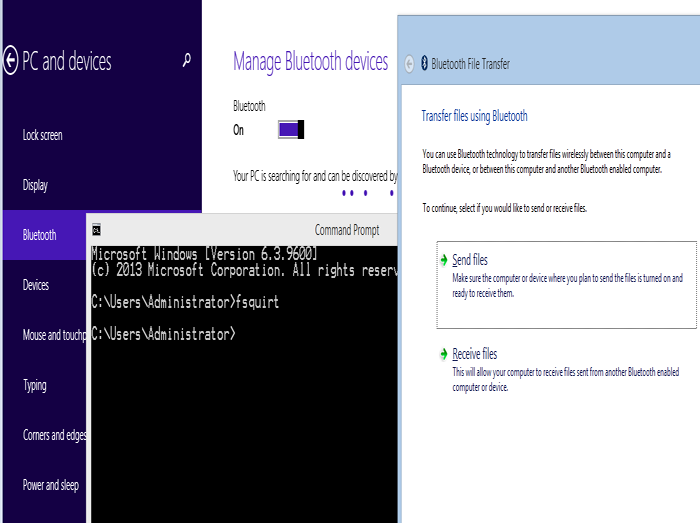
If you're lucky to see the Pair option, it's partially OK. But you'll have to go to this next step:
1) open cmd (type cmd in windows search winkey+Q and open it)
2) type in fsquirt
3) a window will open that says send/receive files via bluetooth
4) enable your PC to receive files from the smartphone you connected before.
It worked for me. Please comment.
Arturo Find for http://www.TurismoAssociati.it/dBlog
You have a Windows 8 operating system on your pc and you noticed there are lots of problems that need a fix...
Your apps can not open for Built-in Administrator account.
You might have encountered with this strange and annoying error. This app can’t open for Built-in Administrator account please sign in with a different account and try again. or while User Account Control is turned off. You need to turn on UAC There is an easy solution for the error.

Solution for Windows 8 App Error:
Hold the Windows key + R and in run dialog box type: secpol.msc
Go to Local Policies –> Security Options –> Scroll down and find "User Access Control: Admin Approval Mode For built in….."
Double click on it and select enabled and the press ok
Again press windows key and R and type regedit
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\UIPI
And on the right hand side double click on default and change the value to 0×00000001(1) and click ok
Restart your computer and all the apps should work.
Do let me know if this has solved your problem. You can give your valuable feedback using the comment box below.
Source: bleepingtech - Author: Anish Sangamam
Some of them are suitable for direct consumption, others can be used to grow your own little psychedelic garden!

All these seeds are good for growing in your own garden or in a pot or plant container. This pack contains 6 different seeds. A nice pack to enjoy a bit of gardening. Besides that we included detailed growing instructions. This way you can grow your own psychedelic garden.
Please note that sometimes a certain seed is out of stock. In that case we replace it with an other kinds of seeds (for example cactus seeds)...
The South American jungle vine Ayahuasca (Banisteriopsis caapi) has a rich history of medicinal and entheogenic use. The word Ayahuasca means "vine of the spirits" in Quechan. In fact many tribes of the Amazon rainforest regarded the vine as a snake that can bear humans into the world of spirits.
The Banisteriopsis caapi vine is the foremost ingredient of Ayahuasca, a traditional psychoactive drink which was used in various religious and healing ceremonies for centuries.
Please note that Ayahuasca is difficult to cultivate from seed and takes a very long time to grow to sufficient size. It's recommended only for the professional cultivator or entheogenic collector.
PLEASE, PLACE YOUR ORDER HERE.
Growing Banisteriopsis caapi
Place the seeds in humus-rich, moist soil (free draining) with the wing end of the seed facing up and uncovered. Water profusely to ensure the soil stays moist. Being from the Amazon, B. caapi only really thrives in moist, tropical climates and does not tolerate any frost, but otherwise it's quite a tough plant.
Sprouting takes between 3 to 4 weeks.

Khat (Catha edulis), also called Qat or Chat, comes from an evergreen tree which grows at high altitudes extending from East to Southern Africa. It's a large shrub which can grow to tree size. It reaches heights from 10 feet to 20 feet and its scrawny leaves resemble withered basil. Fresh khat leaves are crimson-brown and glossy but become yellow- green and leathery as they age. They also emit a strong smell.
The ancient Egyptians considered Catha edulis to be a most sacred plant, a "divine food" like royal jelly to bees, capable of releasing humanities nascent divinity. This plant was so important to the ancients that is was called "the plant" or "the shrub", although its specific name is lost to time. Nowadays khat is used throughout eastern Africa, from the Middle East all the way south, and especially in Yemen, Somalia and Ethiopia it is still popular.
These Khat seeds come from the Nigerian Catha edulis variety and is considered to be of higher quality compared to other sources. With some care the seeds can be cultivated into your very own thriving garden of Khat plants.
Yopo, Anadenanthera peregrina and Piptadenia peregrina are different names for the same plant, which has a rich ethnobotanical history. Not to be mistaken with A. colubrina, or cebil, its use is well documented and covers at least 55 indigenous tribes. The snuff made from the seeds is called cohoba, which has been used in ritual contexts in Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Peru, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico. Many artifacts and administration paraphernalia have been discovered, the long tube, used for blowing cohoba into the nostril of another person, being the most familiar object.

Tripping effects of Yopo seeds
It should be noted that user reports on both yopo and cebil are only rarely precise and correct in describing their ingredients. Most people are not aware of the difference in chemical make up of the two species’ seeds.
Although yopo is taken orally or sometimes even rectally, most people use it parenterally, or through the nose. When snorted, yopo causes a heavy body load in most users. Dizziness, vomiting and headache are common, especially with doses over 3 seeds. Most users also report a dreamlike state of mind or a psychedelic experience, lasting around 15 minutes, with a 30 to 45 minute afterglow.
PLEASE, PLACE YOUR ORDER HERE.
Preparing Yopo for consumption
In order to be absorbed by the body, the seeds must be prepared prior to use:
use 1-4 seeds per person
heat seeds on low heat until they pop
separate the outer seed from the inner seed
the inner part of the seed is used
discard the outer seed shell
heat the remaining inner seed on low
stop heating when it is hard and crunchy
crush the seed (use a coffee grinder, mortar and pestle, etc.)
mix the following: 2 parts seed, 1 part lime or shell, and 1 part baking soda
add a few drops of water to form a paste
mix well and heat on low until material dries
crush dry material into a fine powder (use a coffee grinder, mortar and pestle, etc.)
Fresh seeds will puff up and pop (revealing the inner part of the seed) when lightly heated (may take up to 20-30 minutes). A small pot or pan works well, a lid will help retain heat. After the seed pops, separate the outer seed from the inner seed and discard the outer seed.
The inner part of the seed is then crushed into a powder and mixed with lime (or shells) and baking soda. A small amount of water is added to the mixture to form a paste. Mix the paste well, so that all ingredients are combined together.
Then put it in a pot or pan and supply low heat to evaporate the water from the paste. When the paste dries into a powder, use a coffee grinder or mortar and pestle to crush the mixture into a fine powder that can be snorted.
It may take a while for the mixture to dry, a fan can help speed things up. Edible lime or shell (containing lime) must be added to the mixture in order to be absorbed by the human body effectively. Baking soda added to the mixture will also improve bodily absorption.
The reason cebil or yopo snuff is sometimes blown by a fellow shaman into the nose of the user (see image) is because it is unpleasant. A helper can force a larger amount of the drug into the recipients nasal cavity, than the user would be able to consume alone.
You can make your own inhalation tube with some hollow plant stem or something else that will allow you to inhale the powder you have produced. Most people report a pleasant experience, if the user can overcome the nasal discomfort and nausea.
There will most likely be some degree of an uneasy feeling in the stomach. If you can not force yourself to ingest enough powder to produce the desired effect, a helper can force-blow a large amount of cebil or yopo into your nasal passage. Experienced users say 1-2 seeds worth of powder will have a stimulating effect.
The inhalation of 3-4 seeds worth of cebil or yopo is said to produce a period of stimulation lasting about 20-40 minutes followed by a sedative period where hallucinations will probably be experienced. The first time you try, start with 1 seed (mild) to 4 seeds (wild) worth of snuff and see what you think. A sitter who is not using the drug is a good idea.
PLEASE, PLACE YOUR ORDER HERE.
Dosages between 3-5 seeds have shown to be psychedelic for many users. Dosages over 5 seeds are very high and uncomfortable for most people. One bag contains approximately 40 to 50 seeds.
Ingredients
The seeds of A. peregrina contain N,N-DMT, 5-MeO-DMT and 5-HO-DMT (= bufotenine) (Raetsch 2005).
Warning
This is one of the more experimental herbs available. People who are interested in a DMT experience rather than trying out a certain shamanic method (snorting), are better off with any of the established sources, such as Psychotria viridis or Mimosa hostilis.
Reed canary grass (Phalaris arundinacea)
This plant is also called reed canary grass and is one of the few DMT sources that you can find growing outside in the Netherlands and in other places in- and outside Europe. There is, however, no evidence that this plant has been used as a shamanistic tool or similar. Little research has been done as to how exactly this plant can be used as the DMT source for an ayahuasca analogue.

Nevertheless, there are several positive reports published for this species, most notably by Jim DeKorne. The psychonautic community, judging by Erowid’s Phalaris experience archives, is gradually starting to get involved.
Effects
Nowadays Phalaris arundinacea is primarily used in combination with Peganum harmala to make anahuasca, which is a psychedelic infusion similar to ayahuasca. The effects can best be described as a physical and mental purge, combined with a 4 hour connection with the otherwise imperceptible. The purge is typically not as strong as with ayahuasca, although canary grass apparently causes a lot more nausea and strong discomfort in many users.
The intensity depends on many factors, so many drinkers have to build up some experience and have weak effects in the beginning. When the effects are weak, most drinkers experience something similar to a low dose of psilocybin mushrooms or LSD, combined with stomach cramps in the first 2 hours.
In the case of strong effects, most people experience a drastic change in the interpretation of reality or even some kind of transport of all the senses to another dimension. Anahuasca is known for its strong visions of the bright side and the dark side. The visions tell stories about the drinker and everything else in the universe. Many people don't get visions, however, and experience anahuasca through the other senses. Some people get diarrhoea and have to vomit.
Using an extract of this plant as an incense induces a 15 minute psychedelic experience, borrowing elements from the anahuasca experience, most notably the drastic change in the interpretation of reality or transport of all the senses to another dimension.
Usage
There is only a very small number of recipes available. A safe one would take 15 gr fresh weight for a low dose, 30 for a normal dose and 45 for a high dose. Don't underestimate how overwhelming the experience can be and start with a low dose if you're new to anahuasca. If you are not yet familiar with making the brew, you should know that hardly anyone who makes it for the first time is successful. For most people, making good anahuasca is a result of trial and error and several years of practice. You should read about making anahuasca in books and on the internet (check the links below) and decide on a recipe.
For the purpose of anahuasca, canary grass is run through a wheat grass juicer and its sap is drunk 15 to 60 minutes after taking a 3 to 4 gr P. harmala or 50 to 150 gr Banisteriopsis caapi preparation. A hot water infusion can also be made. Common boiling methods are yet to be established, but simmering the finely cut grass twice on a low fire for 60 minutes in 200 ml of water with 100 ml of lemon juice or vinegar might work. The two infusions are added together and the liquid is boiled down. This extract can also be taken 15 to 60 minutes after taking P. harmala.
P. arundinacea juice from a wheatgrass juicer can also be made into an incense, by boiling the sap down to a tarlike mass.
Growing directions
Cultivation data of this plant for psychoactive purposes is rare. For detailed ordinary growing information, go to PFAF's Phalaris arundinacea page.
For most psychonautic purposes, the seeds can be sprinkled on a layer of soil that is at least 10cm deep. As an indication, keep around 5-10mm distance between the seeds. Gently press the seeds against soil after spreading them evenly. Keep the soil wet, especially in the first couple of weeks after sowing. This plant is easy to germinate, and after a couple months the seedlings are big enough to harvest.
Ingredients
We sell the seeds of P. arundinacea, which are not psychoactive. Once grown, the primary active ingredients in this plant are N,N-DMT and 5-MeO-DMT. It can also have high concentrations of gramine, which is a very toxic alkaloid (C. Raetsch, 2005).
Warning
Take notice of the fact that many Phalaris users report highly unpleasant, uncomfortable experiences and prefer other DMT sources.
When making anahuasca, be aware of the fact that you'll be using canary grass in conjunction with an MAO-inhibiting plant, like P. harmala or B. caapi. MAO-inhibitors can be very dangerous when combined with certain foods or other psychoactives that are totally harmless when taken by themselves.
Don't take P. arundinacea by yourself and please take notice of the historical fact that anahuasca has been used safely in a ritual setting under guidance of trained shamans.
Source: http://azarius.net/smartshop/seeds-of-the-gods/?a=788
These herbs are known for their energizing effects. If caffeine is giving you the jitters and you're looking for a replacement, this is the place to be. Several energy herbs can be used to lose weight.
WHERE TO BUY LEGALLY?
Cha de Bugre (Cordia salicifolia)
Cha de Bugre, or Cordia salicifolia, is used in Brazil for appetite suppression and weight loss. Rather than cutting off appetite altogether, Cha de Bugre gives one a sense of being full and satiated after eating only a few bites of food.
These herbs and extracts are all known for promoting a sensual state of mind and invigorating the body.
Catuaba (Erythroxylum catuaba)
Catuaba is the most famous of all Brazilian aphrodisiacs. Improves potency, enhances sexual excitement and gives more powerful orgasms.
Red Kwao Krua (Butea superba) extract 25x
Butea superba is a herb from Thailand which enhances the male libido and improves the erection. According to user experiences, this natural herb rivals the effects of big brand aphrodisiacs.
WHERE TO BUY LEGALLY?
Damiana Especial (Turnera diffusa)
Damiana Especial is a finer quality of Damiana harvested earlier. This not only makes the herb a lot fresher, it also ensures a younger, more flavourful herb.
A selection of herbs renowned for their hallucinogenic effects. Wormwood, for example, is the basic ingredient for the famous drink absinthe. These herbs can be consumed in different ways, for example by making tea from them or by chewing them well.
WHERE TO BUY LEGALLY?
Absinthe kit
A professional kit to make yourself one litre of absinthe. The absinthe will have the same taste as the original drink from the 19th and early 20th century.
Sinicuichi (Heimia salicifolia) extract 10x
Extract of the sacred, shamanistic Sinicuichi plant from South America. Gives euphoria, relaxation and (auditory) hallucinations.
Source: http://azarius.net/smartshop/herbs/?a=788
|